
Mizan Multispeciality Hospital
Emergency care, also known as emergency medicine, is the medical specialty that deals with the diagnosis, treatment, and management of acute illnesses and injuries that require immediate attention.
Trauma Care: Treatment of injuries from accidents, violence, or other traumatic events.
Cardiac Care: Treatment of heart attacks, cardiac arrests, and other cardiovascular emergencies.
Stroke Care: Treatment of acute strokes and transient ischemic attacks (TIAs).
Pediatric Emergency Care: Specialized care for infants, children, and adolescents.
Psychiatric Emergency Care: Treatment of acute mental health crises, such as suicidal ideation or psychotic episodes.
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR): Life-saving technique for cardiac arrests.
Defibrillation: Use of a defibrillator to restore a normal heart rhythm.
Intubation: Insertion of a breathing tube to establish an airway.
IV Fluid Administration: Administration of fluids and medications through a vein.
Wound Care: Cleaning, dressing, and suturing of wounds.
Emergency Departments (EDs): Hospital-based emergency rooms.
Urgent Care Centers: Community-based facilities for non-life-threatening emergencies.
Ambulance Services: Emergency medical transportation.
Emergency Medical Services (EMS): Pre-hospital emergency care.
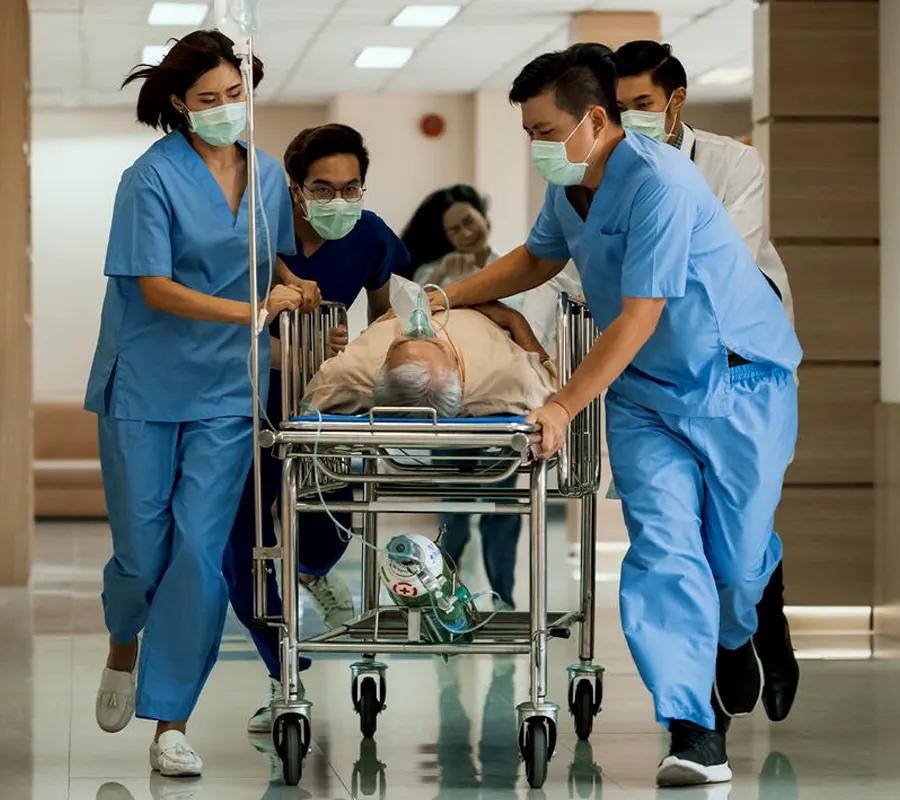
Triage: Initial assessment of the severity of the condition.
Vital Sign Assessment: Measurement of temperature, pulse, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation.
Vital Sign Assessment:Medical History: Review of medical history, allergies, and medications.
Physical Examination: Examination of the patient to identify the source of the emergency.
Treatment Plan: Development of a plan to stabilize and treat the condition.
Mizan Multispeciality Hospital
Anesthesiology is the branch of medicine that deals with the administration of anesthetics to patients undergoing surgery, as well as pain management and critical care.
General Anesthesia: Induces a state of unconsciousness and immobility.
Regional Anesthesia: Numbs a specific region of the body, such as epidural or spinal anesthesia.
Local Anesthesia: Numbs a small area of the body, such as novocaine injections for dental procedures.
Sedation: Induces a state of relaxation and reduced anxiety.
Pain Medicine: Focuses on managing chronic pain.
Critical Care: Provides care to critically ill patients in the ICU.
Cardiothoracic Anesthesiology: Specializes in anesthesia for heart and lung surgery.
Pediatric Anesthesiology: Provides anesthesia care to infants and children.
5. Neuroanesthesiology: Specializes in anesthesia for brain and spine surgery.
Endotracheal Intubation: Insertion of a breathing tube into the windpipe.
Central Line Placement: Insertion of a catheter into a major vein.
Epidural Anesthesia: Injection of anesthetic into the epidural space surrounding the spinal cord.
Nerve Blocks: Injection of anesthetic into specific nerves to numb a region of the body.

Pre-Anesthesia Evaluation: Assessment of medical history, physical condition, and laboratory results.
Anesthesia Administration: Administration of anesthesia, either through inhalation, injection, or topical application.
Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of vital signs, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation.
Physical Examination: Examination of the patient to identify the source of the emergency.
Recovery: Post-anesthesia care, including pain management and monitoring for complications.
Mizan Multispeciality Hospital
Cardiology is the branch of medicine that deals with the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of disorders related to the heart and the circulatory system.
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): Narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries.
Heart Failure: Inability of the heart to pump enough blood to meet the body's needs.
Arrhythmias: Abnormal heart rhythms.
Hypertension: High blood pressure.
Cardiomyopathy: Diseases of the heart muscle.
Valvular Heart Disease: Disorders of the heart valves.
Cardiac Arrest: Sudden loss of heart function.
Electrocardiogram (ECG): Measures the heart's electrical activity.
Echocardiogram: Uses sound waves to create images of the heart.
Stress Test: Measures the heart's function during physical activity.
Cardiac Catheterization: Inserts a catheter into the heart to diagnose and treat conditions.
Cardiac MRI: Uses magnetic resonance imaging to create detailed images of the heart.
Medications: Used to manage conditions such as hypertension, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
Stenting: Inserts a stent to keep the coronary artery open.

Bypass Surgery: Diverts blood flow around blocked coronary arteries.
Pacemakers: Regulates the heart's rhythm.
Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators (ICDs): Prevents sudden cardiac death.
Medical History: Discusses symptoms, medical history, and lifestyle.
Physical Examination: Examines the heart and circulatory system.
Diagnostic Tests: Orders tests to diagnose and monitor conditions.
Treatment Plan: Develops a plan to manage the condition, including medications, procedures, or lifestyle changes.
Mizan Multispeciality Hospital
Critical care, also known as intensive care, is a branch of medicine that focuses on the diagnosis, treatment, and management of critically ill patients who require close and continuous monitoring.
Life Support: Mechanical ventilation, cardiac support, and renal replacement therapy.
Monitoring: Close monitoring of vital signs, cardiac rhythms, and other critical parameters.
Pharmacological Support: Administration of medications to support blood pressure, cardiac function, and other vital systems.
Nutritional Support: Provision of nutritional support to critically ill patients.
Pain Management: Management of pain, anxiety, and agitation in critically ill patients.
Intensive Care Unit (ICU): A specialized hospital unit that provides close and continuous monitoring of critically ill patients..
Cardiovascular Intensive Care Unit (CVICU): A specialized ICU that focuses on the care of patients with cardiovascular disease.
Neurointensive Care Unit (NICU): A specialized ICU that focuses on the care of patients with neurological disorders.
Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (PICU): A specialized ICU that focuses on the care of critically ill children.
Sepsis: A life-threatening condition that occurs when the body's response to an infection becomes uncontrolled.
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS): A condition characterized by inflammation and damage to the lungs.
Cardiac Arrest: A sudden loss of cardiac function that requires immediate medical attention.
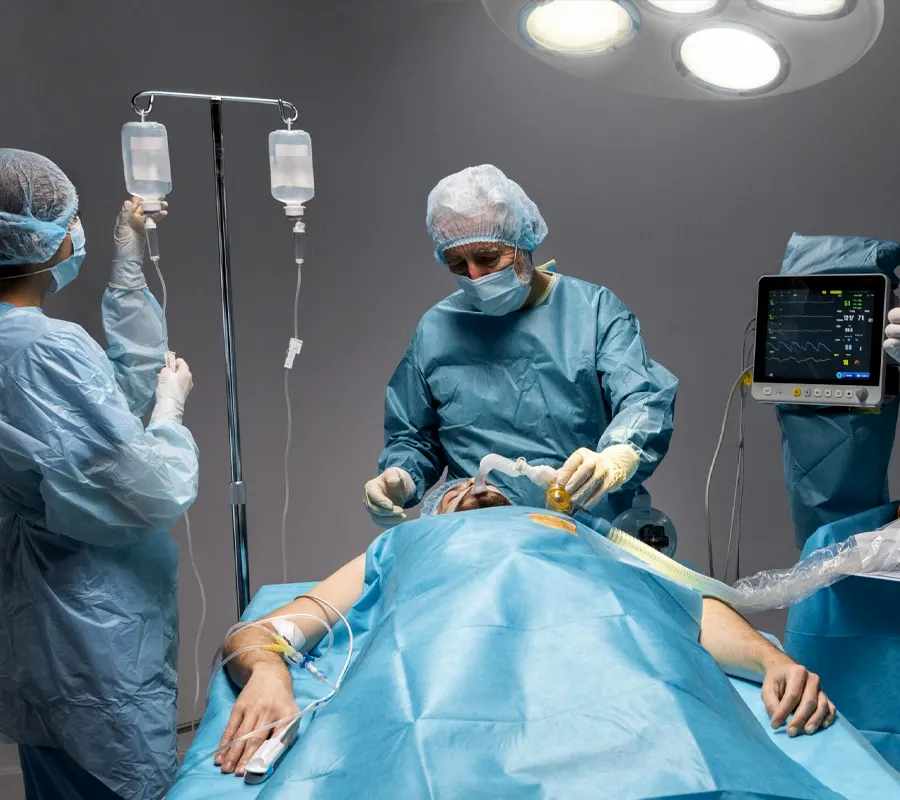
Stroke: A condition characterized by a sudden loss of brain function due to a lack of blood flow.
Trauma: A condition characterized by physical injury that requires immediate medical attention.
Initial Assessment: A thorough assessment of the patient's condition, including a physical examination, laboratory tests, and imaging studies.
Development of a Care Plan: A plan that outlines the patient's treatment goals, interventions, and expected outcomes.
Close Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of the patient's condition, including vital signs, cardiac rhythms, and other critical parameters.
Family Support: Support and education for the patient's family members, including information about the patient's condition, treatment options, and expected outcomes.

